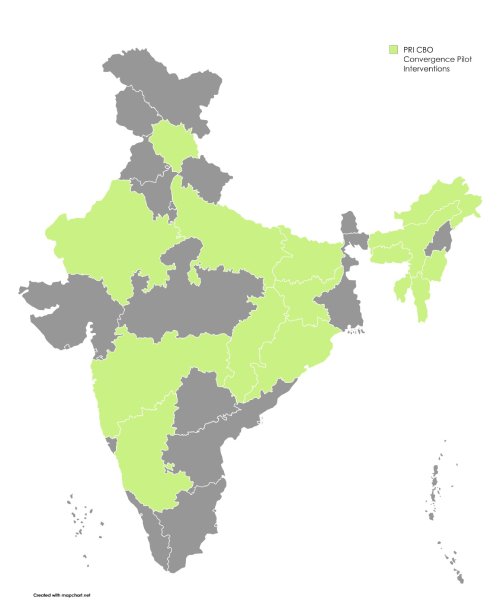
Pilot Interventions
The PRI-CBO Convergence approach is based on the premise that if institutions of the poor such as community-based Based Organisations (CBO) and constitutionally mandated body like Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRI) collaborate with each other to work for the development of the village, they can significantly enhance the livelihood and social security of the vulnerable and poor.
The PRI-CBO Convergence project builds the capacities of PRI and SHG network to work together to strengthen the poor’s access to entitlements and enhance the public’s participation in local governance for improved service delivery. To achieve this, a cadre of motivated community individuals called Local Resource Group (LRG) are nurtured in partner States. The LRGs are expected to work towards enabling convergence of PRI and CBO for the development of the village. As part of the project strategy, the CBOs and PRI are introduced to participatory assessment, planning and monitoring tools to help local communities build awareness and plan for their access to schemes and benefits.
Coverage
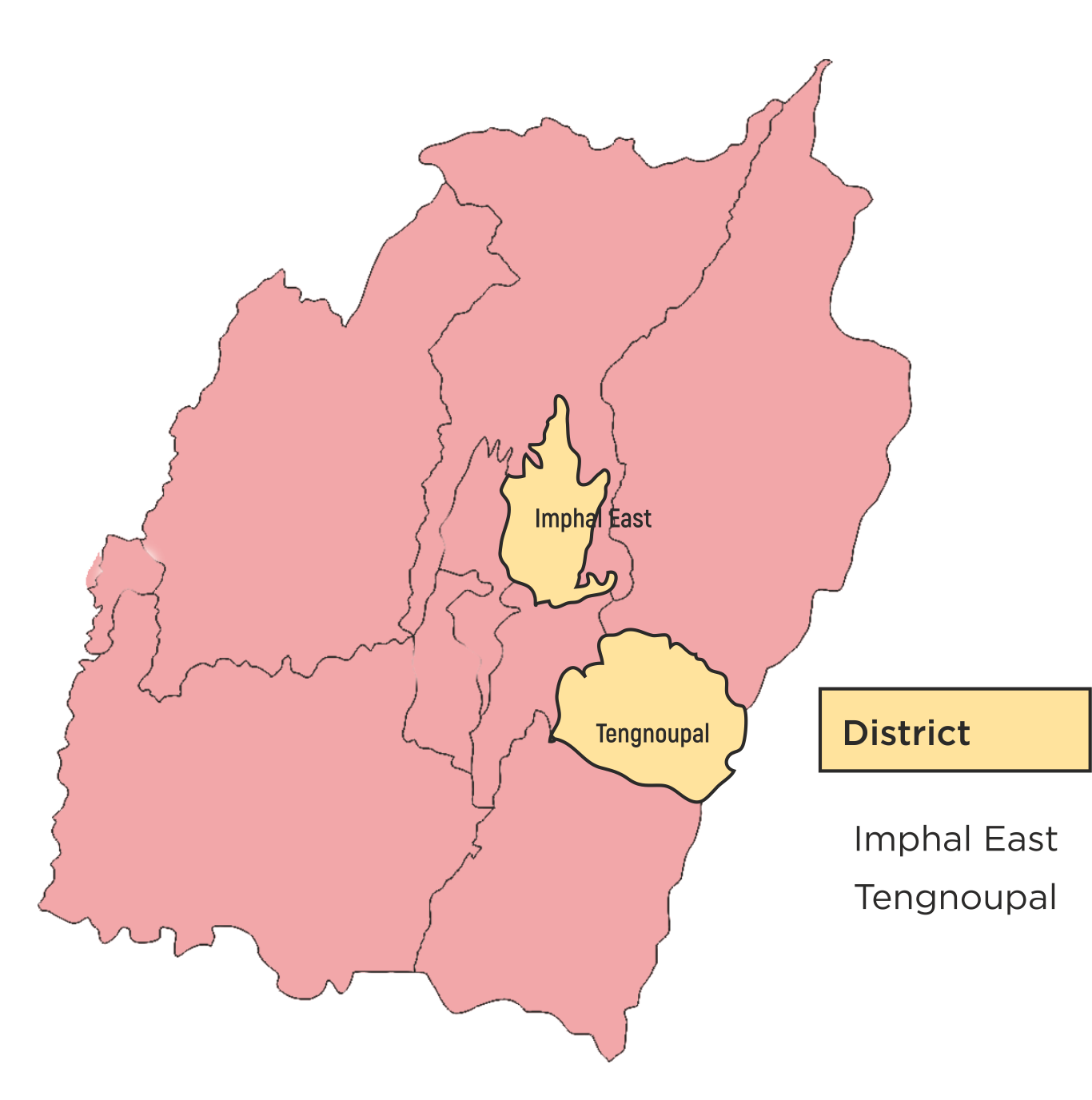
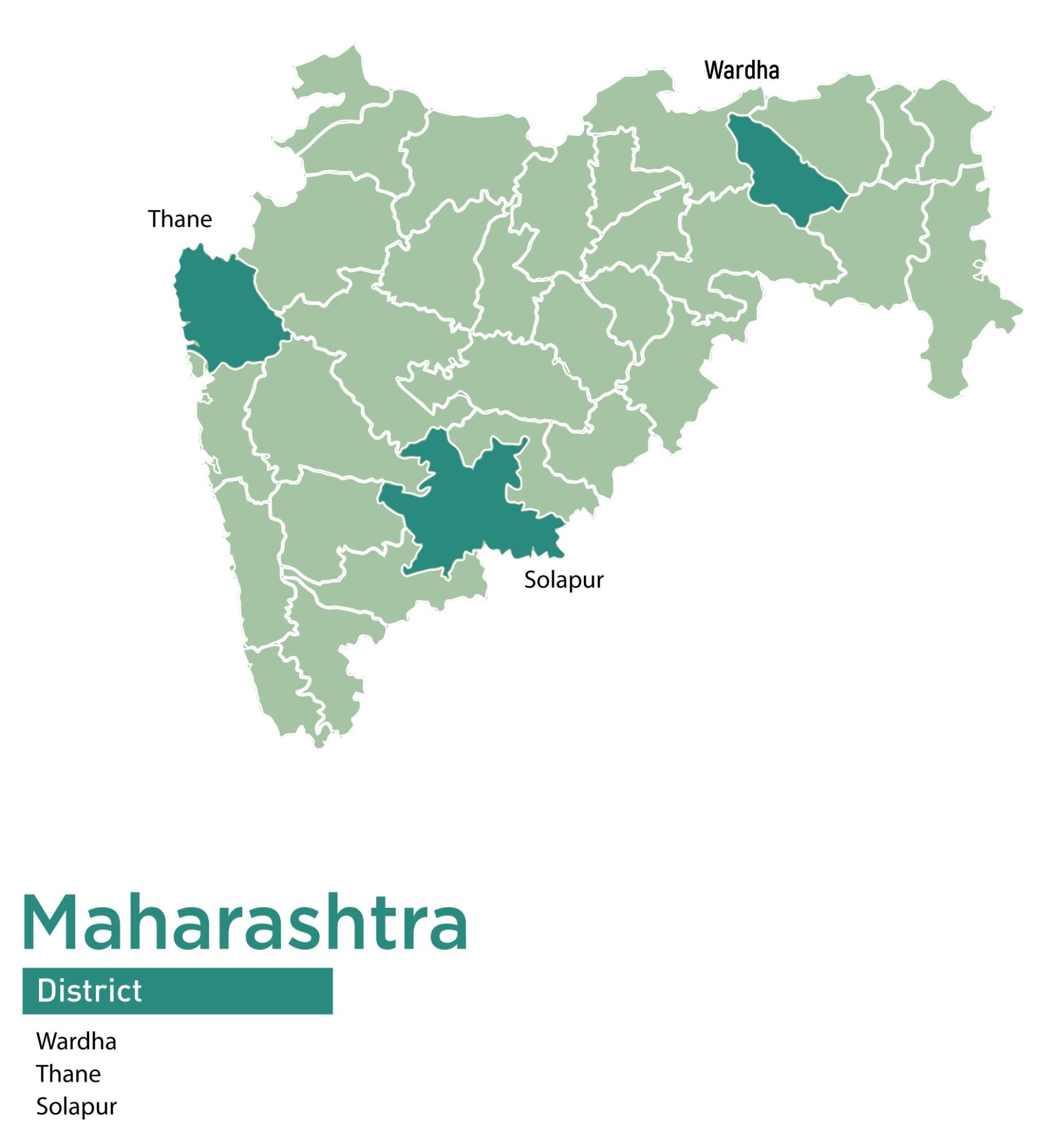
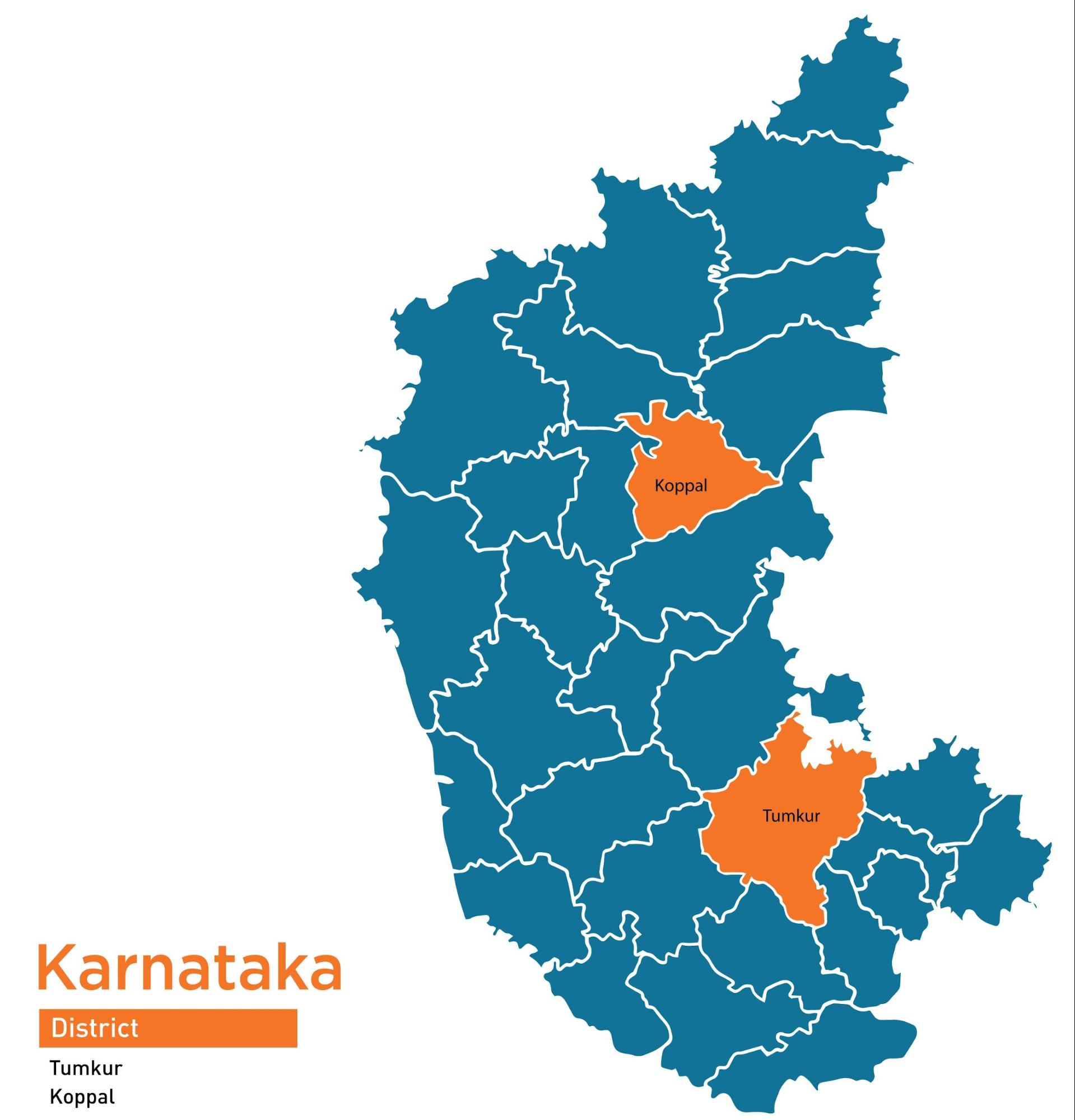
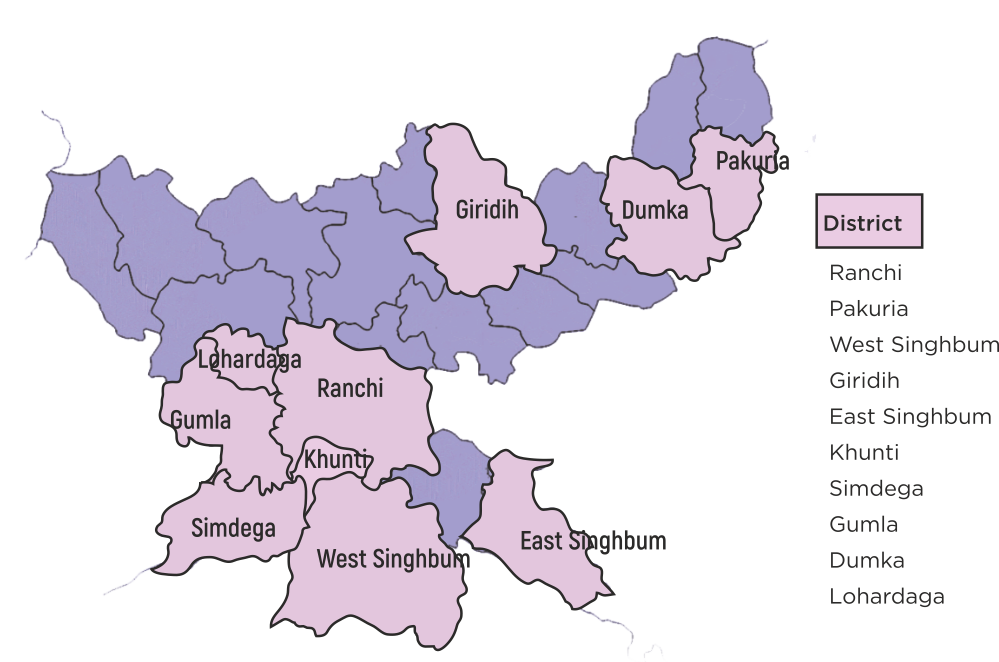
The PRI-CBO Convergence Project has been piloted across 15 states, showcasing effective collaboration between Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and Community-Based Organizations (CBOs). The coverage of the project is as follows:
| Sl. No | State | No. of Districts | No. of Blocks | No. of LSGIs |
| 1 | Maharashtra | 3 | 3 | 58 |
| 2 | Karnataka | 2 | 4 | 40 |
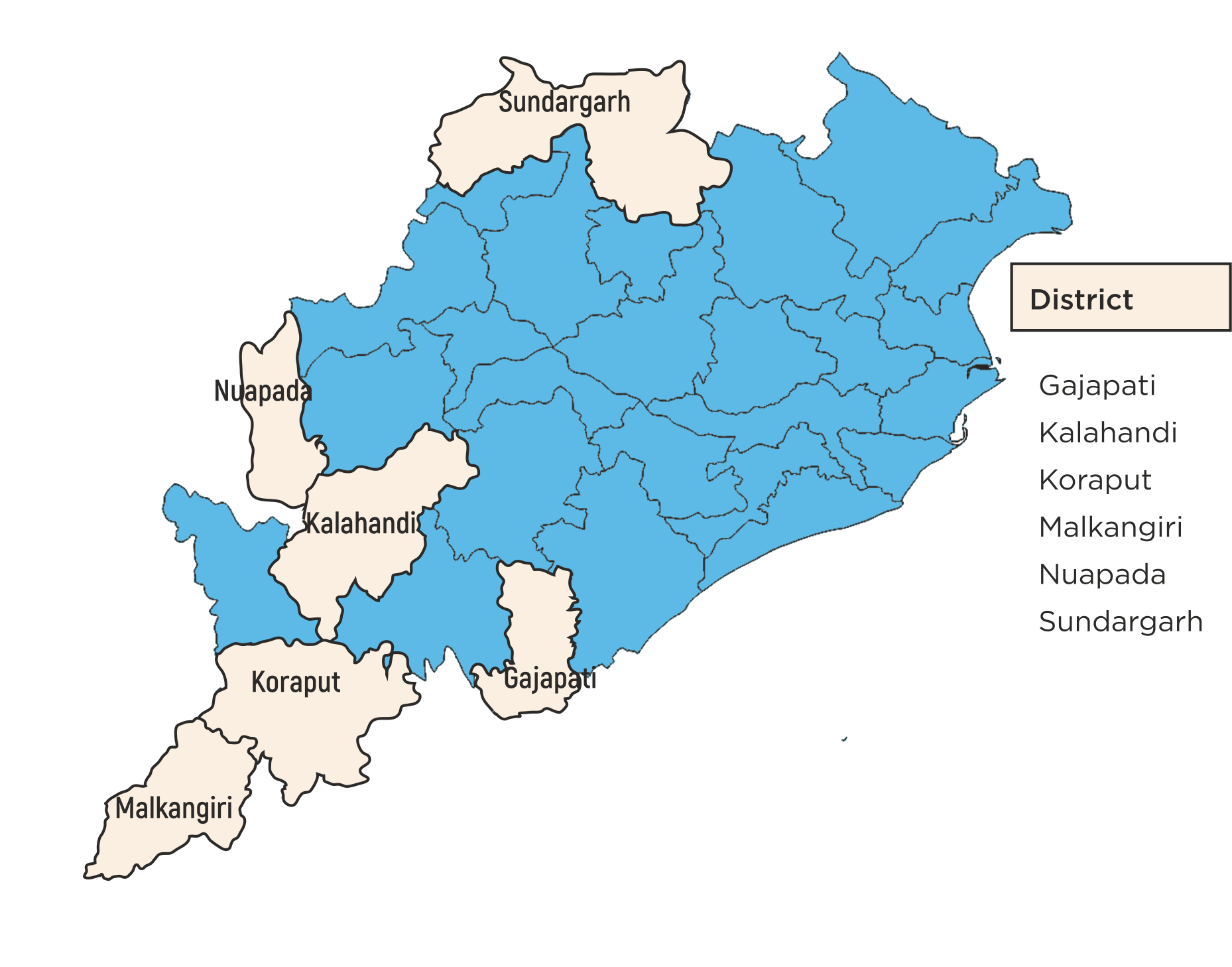
| 3 | Odisha | 4 | 4 | 12 |
| 4 | Jharkhand | 4 | 6 | 617 |
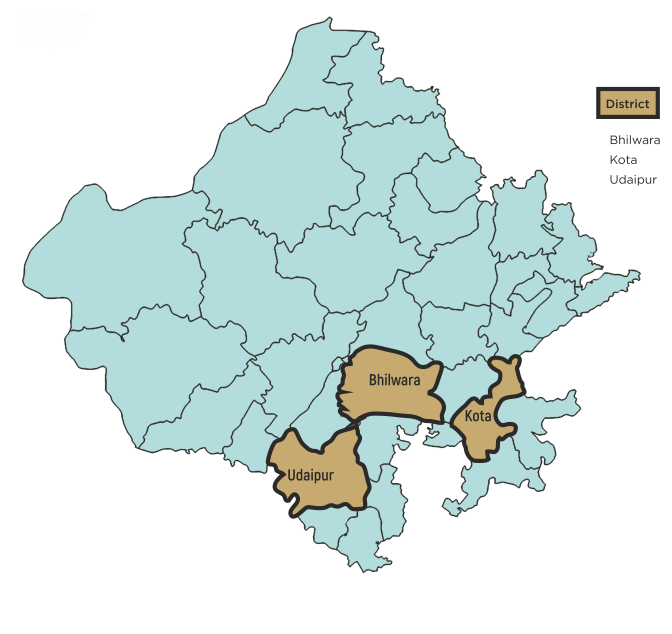
| 5 | Rajasthan | 3 | 4 | 67 |
| 6 | Tripura | 3 | 12 | 347 |
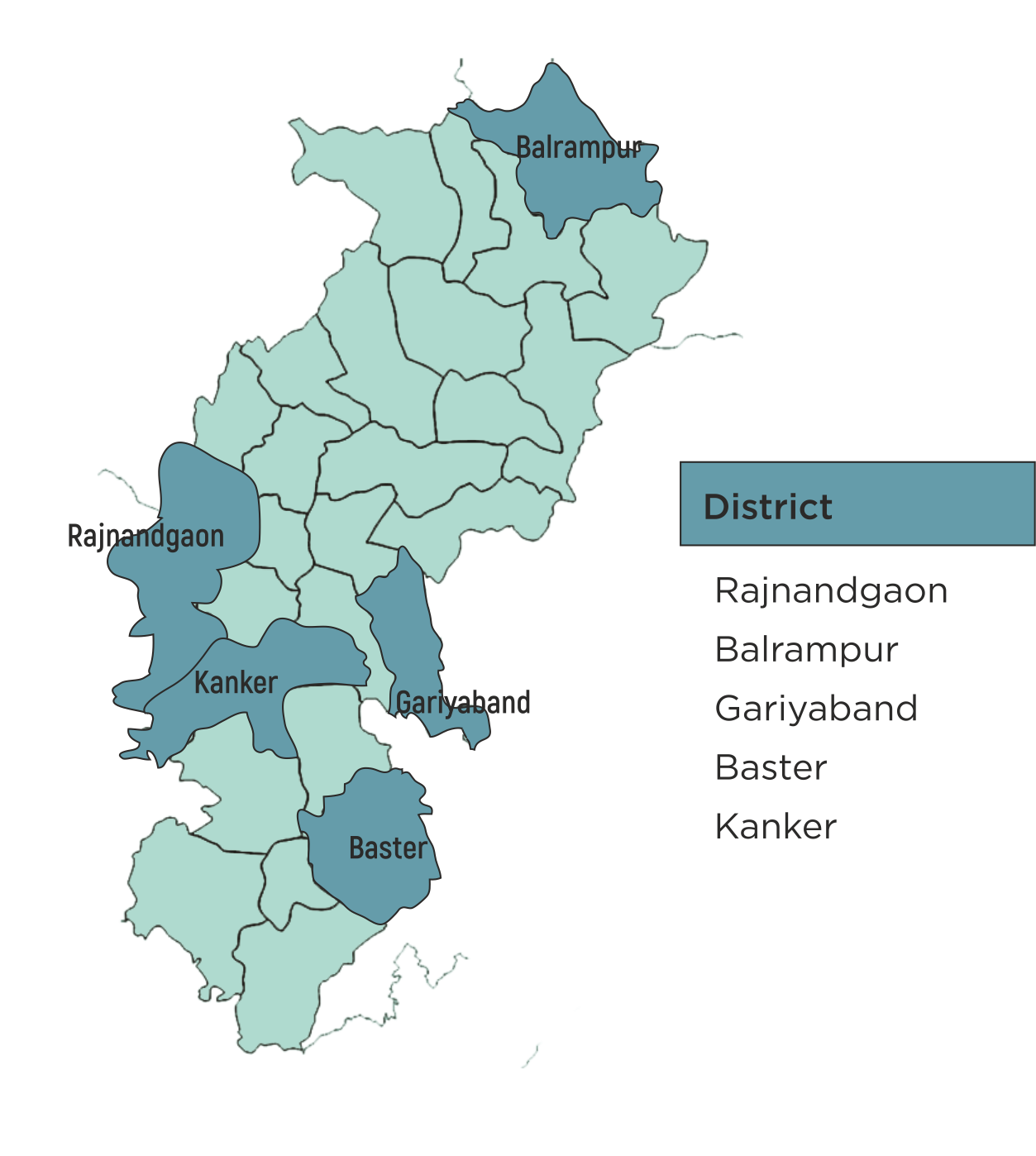
| 7 | Chhattisgarh | 5 | 5 | 87 |
| 8 | Uttar Pradesh | 10 | 10 | 100 |
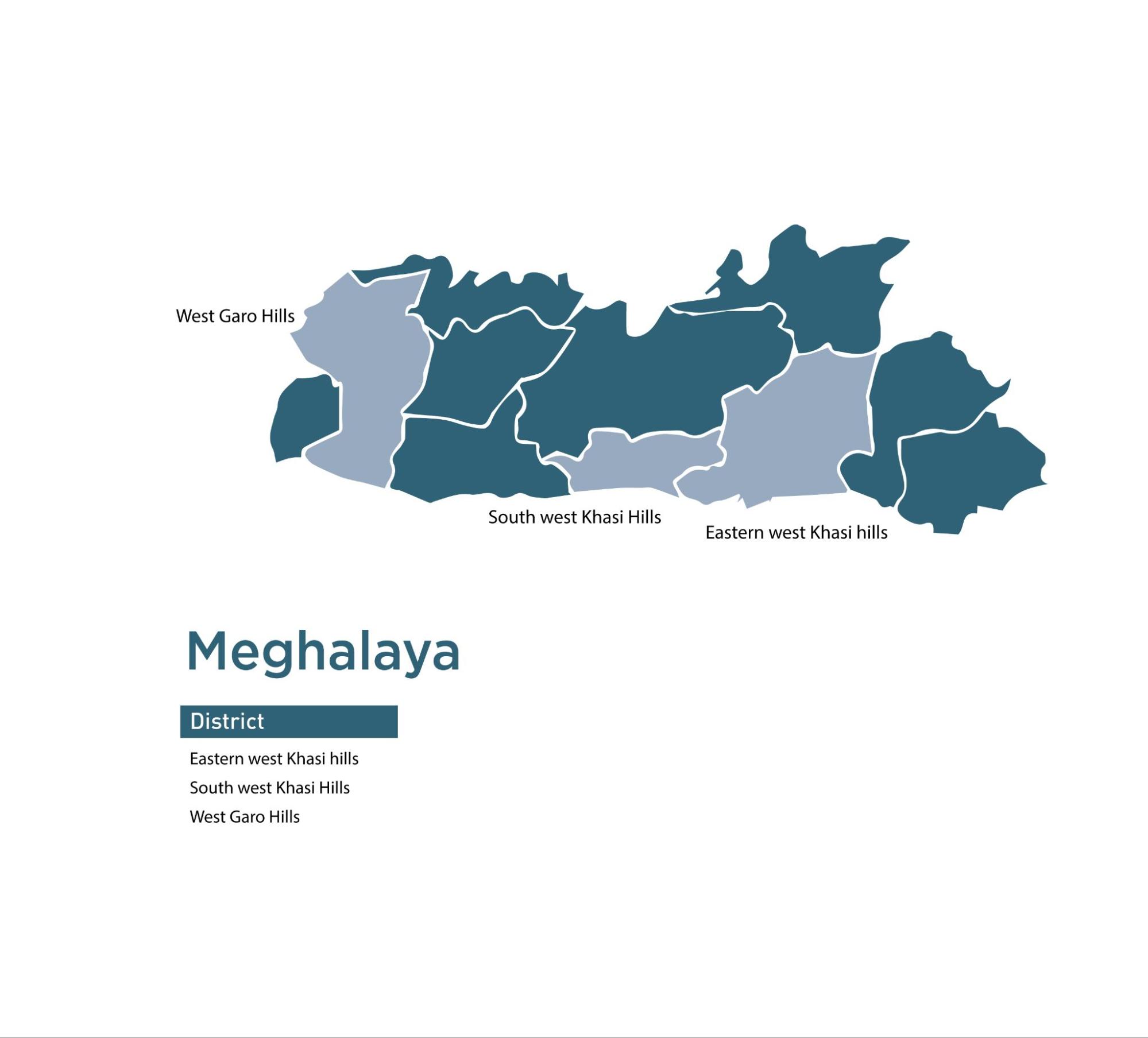
| 9 | Meghalaya | 3 | 4 | 81 |
| 10 | Assam | 16 | 40 | 323 |
| 11 | Manipur | 2 | 6 | 136 |
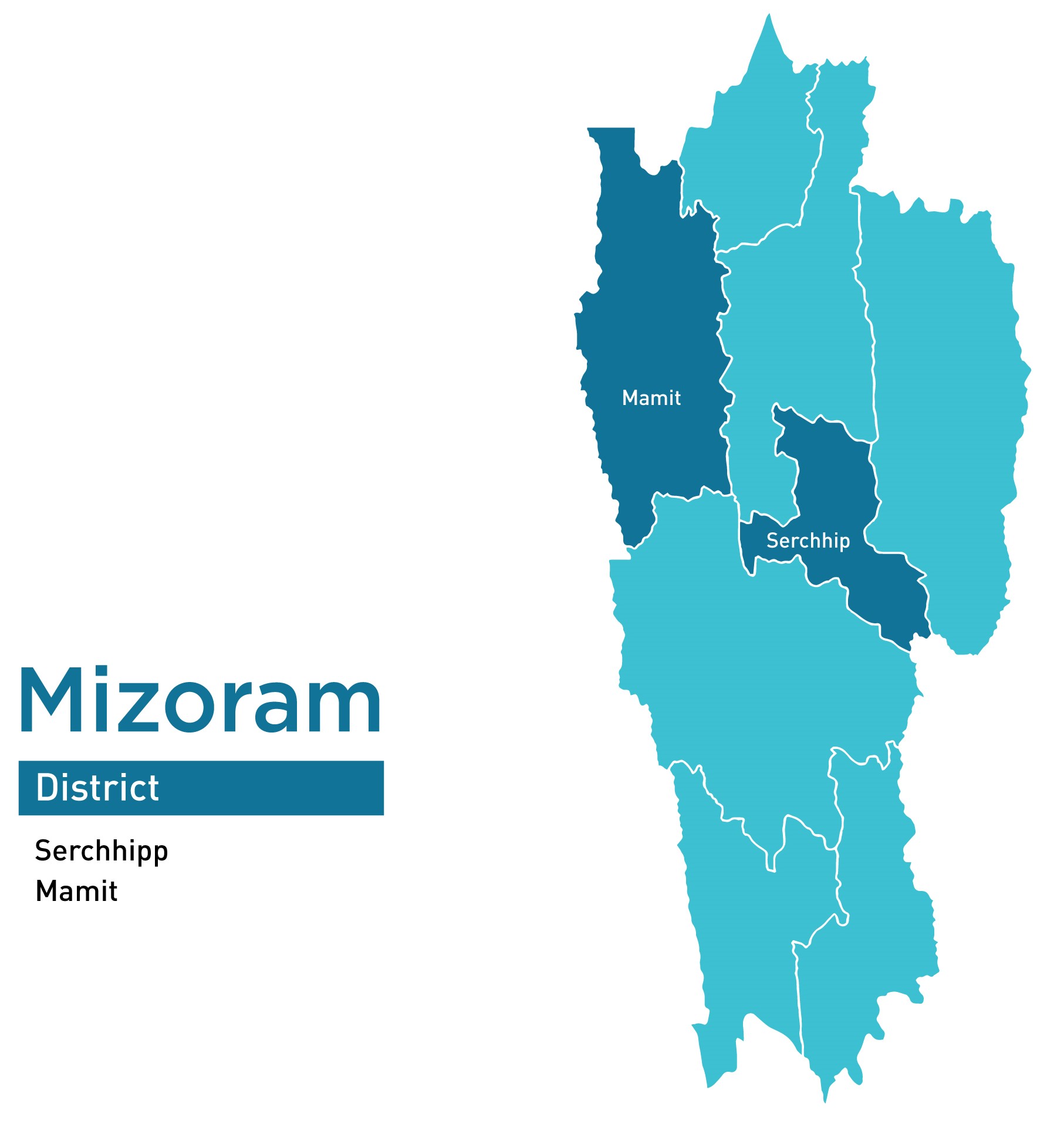
| 12 | Mizoram | 2 | 5 | 78 |
| 13 | Arunachal Pradesh | 4 | 4 | 56 |
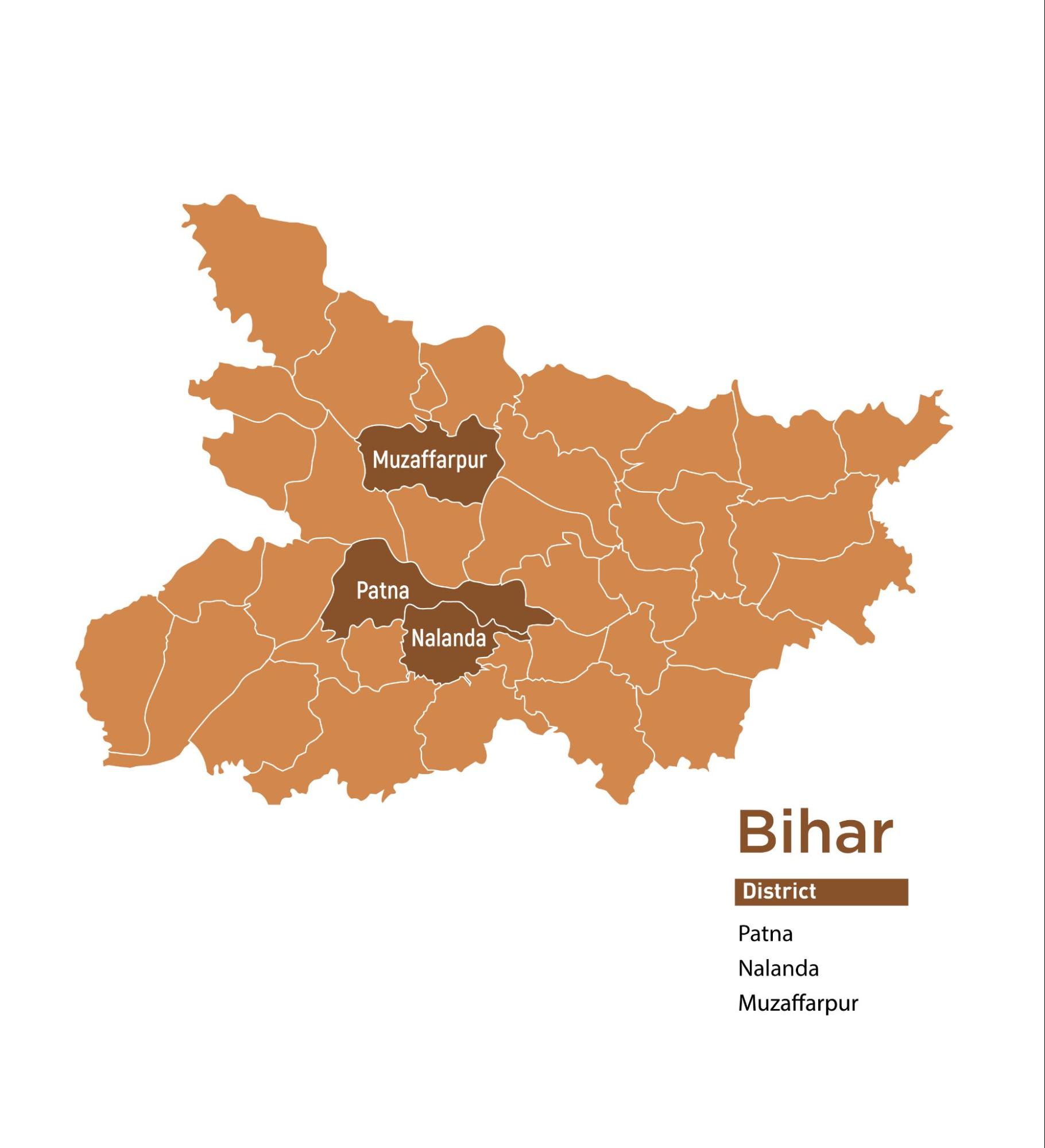
| 14 | Bihar | 3 | 6 | 50 |
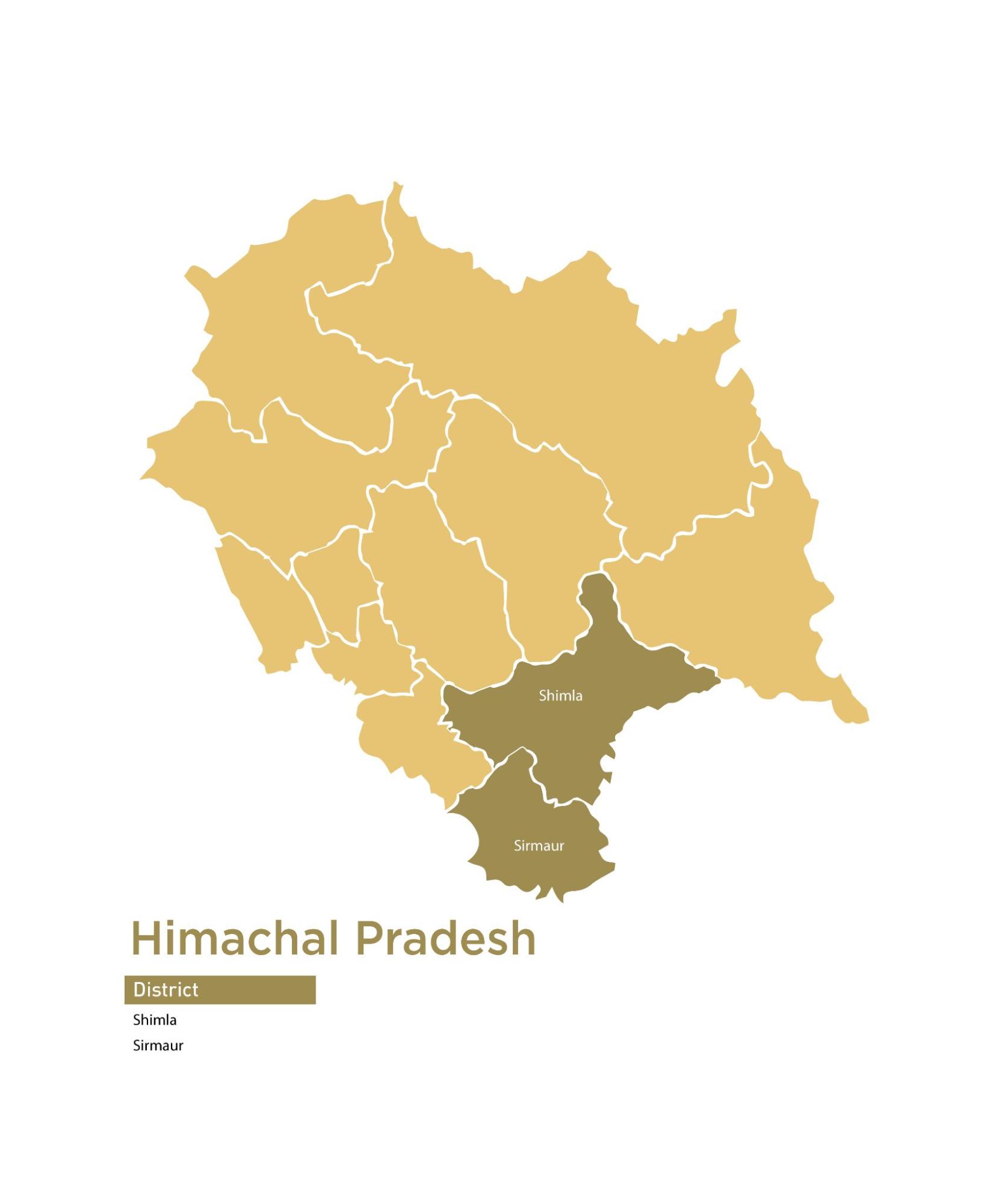
| 15 | Himachal Pradesh | 2 | 2 | 40 |
| Total | 66 | 115 | 2092 | |